The most confusing terms ever made in the Hematology might be the Serum and Plasma which are so frequently used in every assay we perform in the laboratory or whether taking theory lectures, these terms are used everywhere and are not limited to hematology but also frequently used in Biochemistry and Serological studies.
Blood comprises about 7-8% of a person’s total body weight and consists of Liquid and Solid Parts.
The Solid part is mainly the cellular components comprises about 45% of total blood volume which consists of Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, and Platelets whereas the Liquid part that comprises 55% of Total Blood Volume, contains so many substances including dissolved nutrients, Vitamins, minerals, waste substances, nitrogenous products, etc. in Water.

The Serum and plasma, both are the Liquid components of Blood and we can easily get both the things from the person’s Blood.
In most simple words Serum is the liquid part of blood that is devoid of Clotting factors and Cellular components whereas Plasma is the part of blood that only devoid of Cellular parts rest of the things are present in Plasma including Clotting factors.
Serum, as well as Plasma, is commonly used in various laboratory assays including Serological Tests (which includes the examinations of serum for various antigen & Antibodies, etc.), Biochemical Tests like Liver Functions Test, Kidney Function Test, Lipid Profile, Enzymology, Blood Sugar / Glucose Test (preferably Plasma in Fluoride vial), etc.
In the blood vessels of a Living Person, the Blood consists of Cellular part and plasma i.e. liquid part of blood containing Clotting factors but when, somehow, you get injured that clotting factors are activated by a mechanism that forms a clot at the site of injury to prevent the bleeding and blood loss.
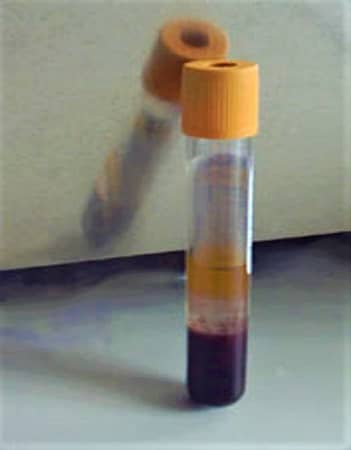
Later, if you see the wound site after the formations of clot a yellowish clear fluid is coming out….. That is the Serum because the clotting factors were used in the formation of a clot at the site of the wound and the liquid left lacks the clotting factor and that is called the Serum.
Now an interesting question arises that why blood doesn’t clot inside our body but once it is out it forms a clot within few minutes and that too in the presence of anticoagulant (Heparin – natural anticoagulant present in blood)???
The Answer to this question is quite simple and various theories were proposed for this.
In Layman language….. In our body, the blood is in Motion or in a mobile state, the heart is continuously pumping out the blood but when it is out of the body in a vial or vessel, it’s in a stationary position as well as the exposure to external environment activates the Clotting factors that result in the formation of a Clot….
The compositions of Serum & Plasma is almost same as both contains Glucose, Hormones, Electrolytes, Antigens, Antibodies, Macronutrients, Micronutrients, and other substances except for the Clotting factors which are present only in the plasma and not in Serum. You can easily remember this with a simple equation i.e.
Plasma – Clotting Factors = Serum
Or
Serum + Clotting Factors = Plasma
If we talk about the separation of Serum and Plasma from the Blood, then the difficulty level is almost similar, however, if we are going to separate serum then we have to be more patient because it takes some time for the formation of an ideal clot to get a pure serum.
Check out the 21 Difference Between Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RED BLOOD CELLS AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS (RBCs VS. WBCs)
On the other hand, to obtain plasma from the blood we need to add proper anticoagulant to the Blood as per the Tests to be performed and that too in an appropriate proportion to avoid any error in results.

Here I m gonna explain top 15 difference Between Serum and Plasma
S. No. FEATURES SERUM PLASMA
1.) Definition A yellowish fluid obtained from the blood after the formation of clot. A yellowish fluid obtained from the blood in which blood cells are freely present without any clot
2.) Historical Aspects It was first Discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901 when he was finding different types of blood groups and realized that the effect was due to the presence of Serum. In 1918, Gordon R. Ward discovered the use of Plasma for transfusion purposes.
3.) Method of Separation The Serum is separated by centrifugation after Clot Formation. The Plasma can be obtained any time once the Sample is taken in Anticoagulated vial containing appropriate Anticoagulant in right proportion.
4.) Constituents Serum contains all the Proteins, Metabolites, Hormones, Electrolytes except for cells and clotting factors. In plasma, All the Proteins, Metabolites, Hormones, Electrolytes as well as Clotting factors are present.
5.) Density The density of Serum is slightly low as compared to Plasma that is 1.024 gm/ml The density of Plasma is 1.025 gm/ml
6.) Water Content In Serum about 90% water is present. Plasma consists of about 92-95% water.
7.) Fibrinogen Fibrinogen is not present in Serum as it is used during the formation of clot Fibrinogen is present in Plasma.
8.) Use of Anticoagulant Anticoagulant is not required to separate the Serum as Anticoagulant prevents the Clotting of blood. Anticoagulant is required if you wanna obtain plasma as Anticoagulant prevents the Clotting of Blood.
9.) Cellular organization In Serum, the blood cells sticks together and forms a mesh-like structure that is commonly called as a Clot In Plasma, the cells are freely suspended in the Plasma and mesh-like structure or clot is Absent.
10.) Clotting Factors Absent as they're used up during clot formation. Present as no clot formation takes place.
11.) Difficulty of Extraction The separation of Serum from the Blood specimen is tiresome, requires expertise and more time consuming than Plasma separation The plasma separation is quite easy and can be obtained in just a minute or two.
12.) Storage Stability A serum sample can be stored at 2-6 Degree Celsius for few days or maximum for a week or at -80 degree Celsius for longer period of time (few months approx.) Same guidelines as for Serum
13.) Medical Use Serum therapies are widely used for the treatment of Hair problems, Chronic Urticaria etc. Plasma is commonly transfused in the patients suffering from Hemophilia, Burn patients and Clotting Disorders.
14.) Diagnostic Use Serum is widely used in the various Serological tests for the identification of various causative agents of diseases as well as for Blood Group testing and Cross Matching. Also Serum is used for the various biochemical parameters and electrolyte estimation. Plasma is commonly used in hematology laboratory for Blood grouping, Cross matching, HbA1c test, as well as Estimation of Sugar etc.
15.) Discoloration On prolonged storage, the serum sample does not Discolorize. On prolonged storage, the Plasma sample tend to Discolorize.
That’s All about the Difference Between serum & plasma
Further Reading:

Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.
Thanks
Most Welcome 🙂
Very informative notes.. Thnx a lot
Appreciate the effort. Nice content and loved reading this.