In this section, We are providing you the quality study notes of every single virus where you will learn about the morphology of viruses, their characteristics, and classification, what are the requirements of individual virus for the growth and cultivation in the laboratory, the pathologies they cause in human body, the laboratory diagnosis of viral diseases, treatment of viral infections and the effective prophylactic measures for the prevention of viral infections and if you got stuck anywhere or have any queries about any topic contact us here and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Click on the links given below to learn more…..

INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) ⇒ HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus is the causative agent of AIDS, the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. ⇒ This syndrome was first observed in 1981 & isolated in 1983. ⇒ HIV is the member of Lentivirus Genus of the Family Retroviridae. ⇒ Members of Retroviridae possess reverse transcriptase (RNA directed DNA polymerase) enzyme which prepares the DNA copy of RNA genome (of the virus) ...

INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS VIRUS ⇒ Viral hepatitis is a systemic disease with primary inflammation in the liver by any one of a heterogeneous group of hepatitis viruses. ⇒ There are six hepatitis viruses i.e., hepatitis A, B, C, D, E & G. ⇒ The designation ‘type F’ had been proposed for a putative virus believed to cause transfusion-associated hepatitis, later proved to be the mutant (HBx) of the type B ...

INTRODUCTION TO POX VIRUSES Pox viruses are the largest and the most complex of all viruses, belongs to the family poxviridae and causes a number of diseases, are large enough to be seen under the light microscope. MORPHOLOGY OF POX VIRUSES ⇒ Poxviruses are brick-shaped. ⇒ Genetic Material – dsDNA ⇒ Poxviruses have complex symmetry. ⇒ Largest animal viruses of size – 300*200*100 nm. ⇒ Enveloped viruses. ⇒ Poxviridae consists ...
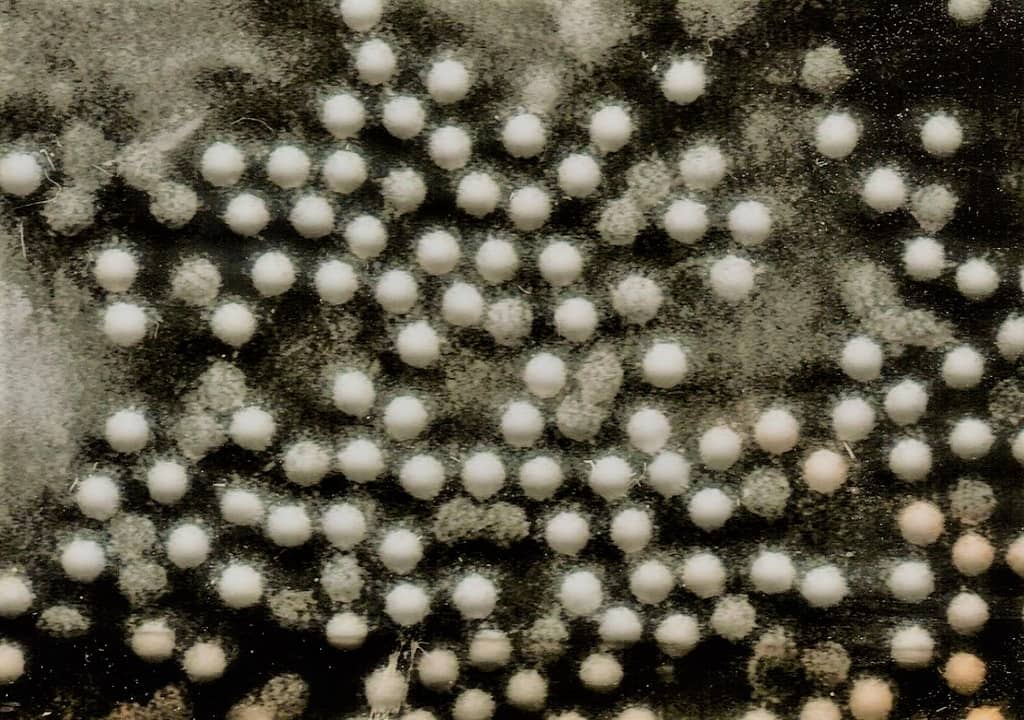
INTRODUCTION TO POLIOVIRUS Poliovirus is the causative agent of poliomyelitis, an acute infection that affects the CNS i.e. the brain and spinal cord. MORPHOLOGY OF POLIOVIRUS ⇒ Polio virus belongs to Enterovirus genus of Picornaviridae ⇒ Polio virus is a Spherical, Enveloped virus, composed of 60 subunits, each consisting of four viral Proteins – VP1 – VP4, arranged in icosahedral symmetry. ⇒ Size: 27-30 nm. ⇒ Genetic material – ssRNA ...

INTRODUCTION TO INFLUENZA VIRUS ⇒ Influenza virus is an Orthomyxovirus, belongs to family orthomyxoviridae; causes influenza, an Acute Respiratory illness. ⇒ Orthomyxoviruses are spherical or filamentous, enveloped viruses with single-stranded RNA genome, that causes Respiratory illness. ⇒ Orthomyxoviruses have the ability to adsorb onto mucoprotein receptors on RBCs, causing haemagglutination. MORPHOLOGY OF INFLUENZA VIRUS ⇒ Influenza virus is a Spherical or Pleomorphic or Filamentous, Enveloped virus having a helical nucleocapsid. ⇒ ...
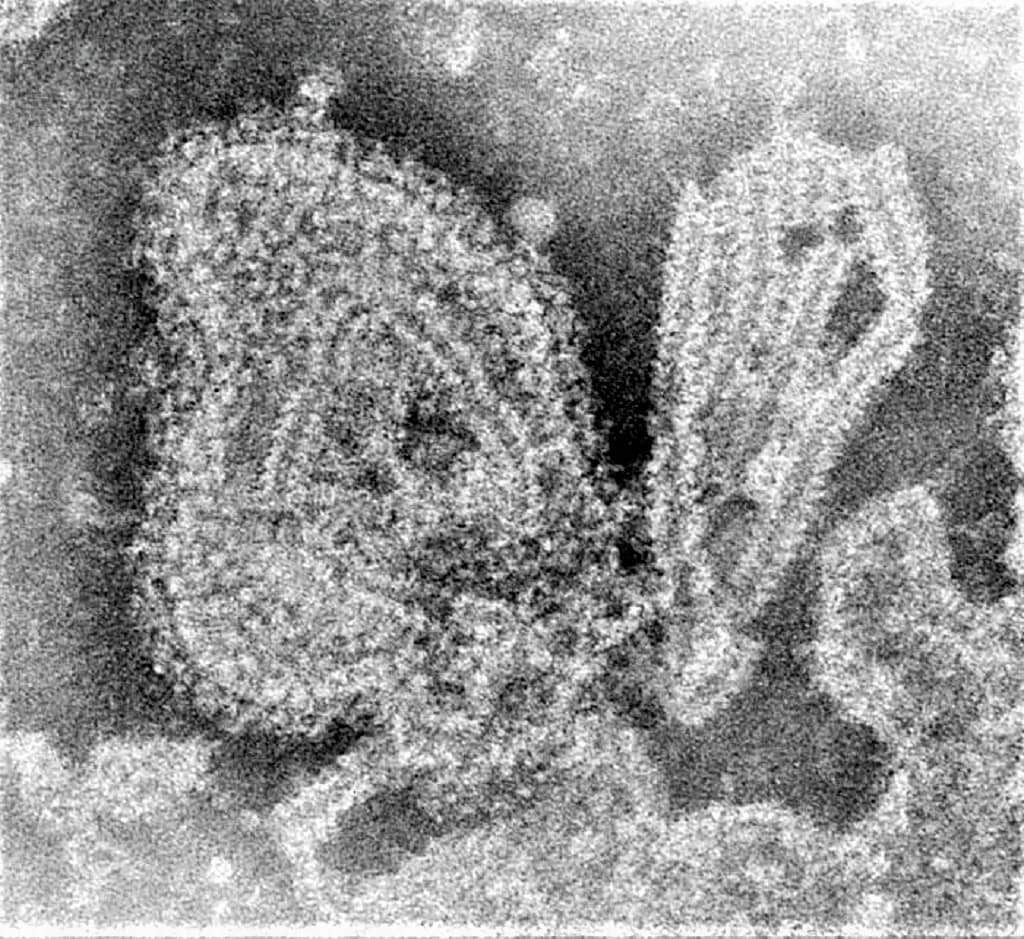
INTRODUCTION TO MUMPS VIRUS ⇒ MUMPS VIRUS is the causative agent of disease MUMPS, an acute infectious disease commonly affecting children and characterized by Parotitis (inflammation of parotid glands). ⇒ It had been described by Hippocrates in the fifth century BC as ‘Epidemic Parotitis’. ⇒ This virus belongs to the Rubulavirus genus of Paramyxoviridae MORPHOLOGY OF MUMPS VIRUS ⇒ It Resembles orthomyxovirus in morphology – Spherical, Enveloped virus with helical Nucleocapsid ...
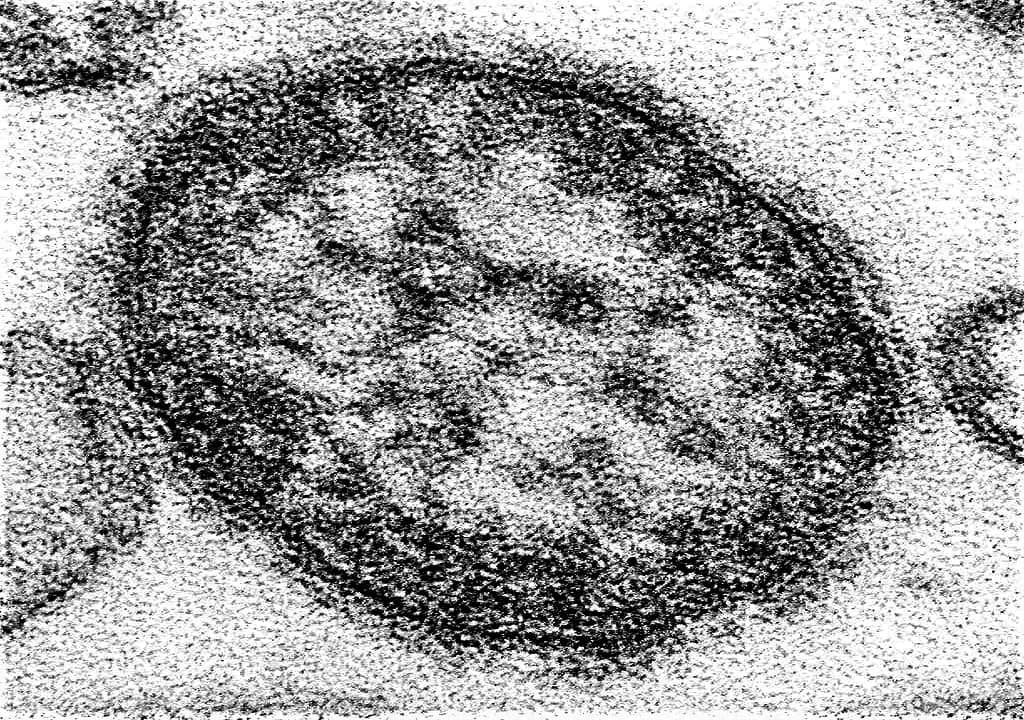
INTRODUCTION TO MEASLES VIRUS ⇒ MEASLES VIRUS is the causative agent of disease Measles, a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory system. ⇒ It had been described by Thomas Sydenham in 1690. Later, in 1954, it was first isolated in monkey and human kidney cells by Enders and Peebles. ⇒ Measles virus belongs to the Morbillivirus genus of Paramyxoviridae family. MORPHOLOGY OF MEASLES VIRUS ⇒ Resembles orthomyxovirus in morphology – Spherical, ...
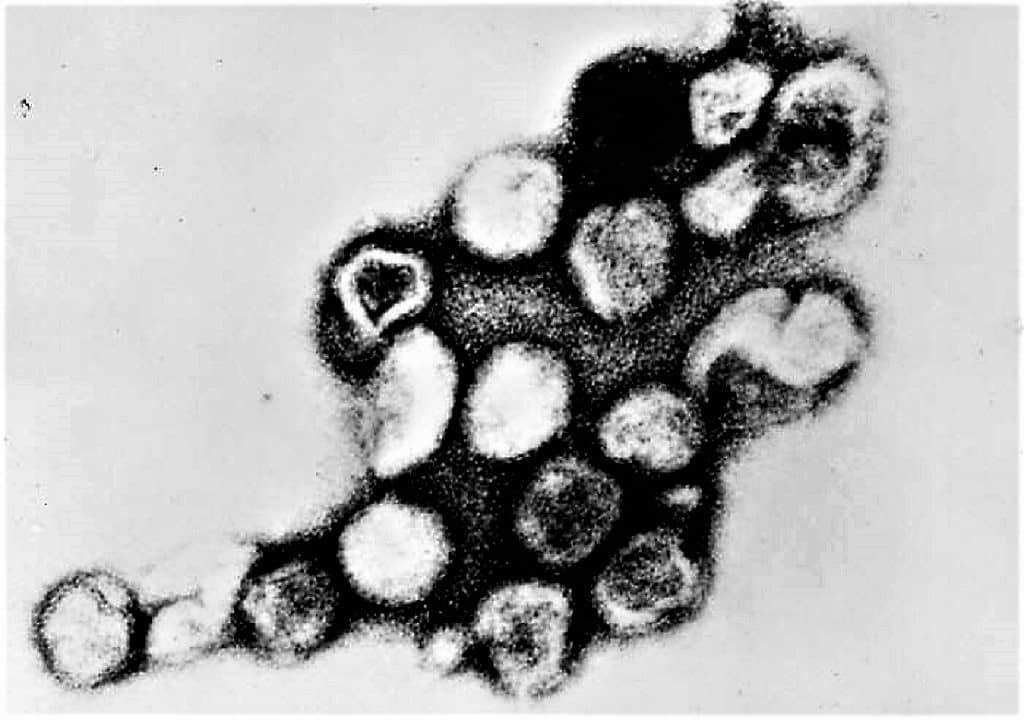
INTRODUCTION TO RUBELLA VIRUS ⇒ RUBELLA VIRUS is the causative agent of disease Rubella or German measles, a mild exanthematous fever which may be acquired Congenitally or Postnatally. ⇒ It was first described by an Australian Ophthalmologist Gregg in 1941 & was first isolated in tissue cultures in 1962. ⇒ This virus belongs to the Rubivirus genus of Togaviridae Family. MORPHOLOGY OF RUBELLA VIRUS ⇒ Rubella virus is pleomorphic, roughly spherical ...

INTRODUCTION TO HERPES VIRUS ⇒ HERPES VIRUS is the family of viruses, contains hundreds of viruses, maximum of which infects humans. ⇒ They are characterized by their ability to establish latent infections, enabling the virus to persist indefinitely within the hosts and to undergo periodic reactivation. MORPHOLOGY OF HERPES VIRUS ⇒ Herpes virus is spherical & enveloped virus containing icosahedral capsid. ⇒ The capsid is composed of 162 capsomers & ...
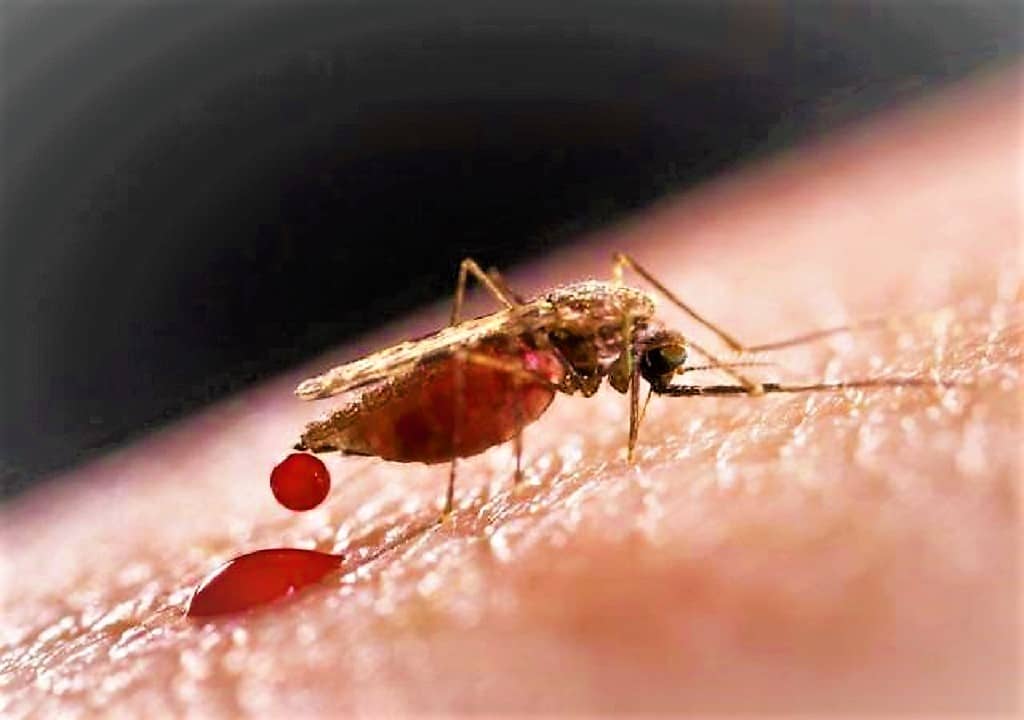
INTRODUCTION TO ARBOVIRUSES ⇒ Arboviruses are the RNA viruses that are transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods from one vertebrate host to another ⇒ Arboviruses are worldwide in distribution but are more numerous in the tropical than in temperate zones. ⇒ Arboviruses are very wide host range including many species of animals and birds. The most important arbovirus vectors are mosquitoes, followed by the Ticks. CLASSIFICATION OF ARBOVIRUSES CHARACTERS OF ARBOVIRUS FAMILIES ...

INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS (RSV) ⇒ The Respiratory syncytial virus is the most important causative agent of bronchiolitis & pneumonitis in infants and causes common cold or rhinitis in older children and adults. ⇒ RSV was first isolated in 1956 from chimpanzees with coryza & was called the chimpanzee coryza agent. ⇒ A year later, the virus was obtained from children with lower respiratory tract infection and found associated with ...
Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.











