A variety of techniques has been developed for the isolation of microorganism, mainly the bacteria, from the specimen or from the cultures and Streak plate technique is among the most widely used technique to obtain discrete & Well developed colonies of microbes.
The Culture techniques are commonly used in the laboratory for various purposes for which they are intended. The indications for the culture of the organism is mainly done –
- To demonstrate the cultural characteristics of the bacteria (e.g. color, texture, size, elevation etc.).
- To isolate the bacteria in discrete colonies from the specimen containing more than 1 bacterium.
- For determining the Sensitivity and/or Resistance of bacterium towards the particular Drug/Antibiotics or Test substances.
- To obtain the sufficient growth of the bacterium for various biochemical and other tests.
- To estimate the viable counts of the bacteria in the specimen.
- To maintain the stock cultures.
- For transportation of biological materials or short-term storage of the specimen (e.g. stab culture).
Three types of techniques are commonly employed for the isolations of microorganism from the specimen which are as follows:
- Pour Plate Technique
- Spread Plate Technique
- Streak Plate Technique
In this article, we’ll discuss the Streak Plate technique for the isolation of microorganism in the microbiology laboratory.
Check out the Pour Plate Culture Technique for isolating the microorganism
POUR PLATE CULTURE TECHNIQUE FOR THE ISOLATION OF MICROORGANISM / BACTERIA IN PURE CULTURE
PRINCIPLE OF STREAK PLATE TECHNIQUE
The Streak Plate technique for the isolation of microorganism is the most practical method of obtaining discrete and well-developed colonies of the microbe in pure cultures.
It was originally developed by the two bacteriologists, Loeffler and Gaffkey in the lab of Robert Koch (Father of Bacteriology).
In Streak plate technique, a sterilized loop or transfer needle is dipped into the mixed culture of the specimen or a suitably diluted suspension of organisms or Broth cultures, which is then streaked on the surface of Sterile Media plates to make parallel, non-overlapping streaks which are then incubated at optimum temperatures for 24-48 hours usually (for bacteria) or for few weeks in case of fungi.
The Aim of this method is to obtain the discrete, well-developed colonies of the microorganism that are pure, i.e. the growth derived from the single bacteria cell/spore.
Check out the Spread Plate Culture Technique for isolating the microorganism
SPREAD PLATE CULTURE TECHNIQUE FOR THE ISOLATION OF MICROORGANISM / BACTERIA IN PURE CULTURE
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE POUR PLATE TECHNIQUE
- 24 hours old nutrient broth culture of two or more bacteria (Mixed Culture) or Sample/Specimen.
- Nutrient Agar Medium
- Six 9 ml Sterile Water Blanks
- Sterile Petri plates
- Graduated pipette (1ml or 1000 ml)
- Bunsen burner or Spirit lamp
- Marker
PROCEDURE OF SPREAD PLATE TECHNIQUE
⇒ Prepare the Nutrient agar medium (NAM) and label the sterile Petri plate with the Patient identification no. & Date.
LEARN: How to prepare Nutrient Agar Medium in Laboratory?
⇒ Now, pour the prepared Nutrient Agar Medium into the Sterile Petri plates under strict aseptic conditions. Allow the Media plates to Solidify.
Usually, the Streak plate method is done by streaking the specimen directly onto the Agar media plates but in some cases when the there is the more dense population of the organism in the specimen is suspected that a serial dilution of the specimen is done and then the diluted specimen is streaked onto the solidified agar media plates.
Follow the dilution step if required otherwise directly follow the Streaking protocol (T streak method or Quadrant method)
Serial Dilutions of the Specimen / Sample
⇒ Label the 6 Sterile Water blanks (9ml sterile water in each tube) as number 1 to 6 with the help of Marker. Also, label the Sterile Petri plates as number 1 to 6. Pour the Agar media in the plates and Kept aside to Solidify.
⇒ Place the labeled tubes in the test tube rack. Mix well the 24 hours old broth culture to equally distribute the bacterial cells in the tube.
⇒ After mixing, Remove the Cotton plug and aseptically transfer the 1 ml of the bacterial suspension from the tube of culture to sterile water blank tube no. 1 using a graduated pipette.
⇒ Shake the tube no. 1 to mix well the content to uniformly distribute the bacterial cells. Transfer the 1 ml of this to the water blank tube no. 2 by using the graduated pipette.
Note: Use the separate sterile pipette each time to transfer the contents from one tube to another.
⇒ In this way, make serial dilutions till the six water blanks (no. 1 to no. 6).
Inoculating / Streaking the Specimen on Media plates
There are various methods or patterns of streaking have been developed for inoculating the specimen on the media plates for the isolation of microorganisms.

But three methods are commonly used in most of the microbiology laboratories for the isolation of microorganism in pure cultures which are as follows –
- Parallel Streaking method (Quadrant)
- Zigzag streaking method (Quadrant)
- T streak Method (Three sectors)
The parallel Streak Quadrant Method & Zigzag Streak Quadrant Method are the Quadrant methods whereas the T- Streak method is the three sector method.
The Parallel Streak Quadrant method is commonly used in the Labs for the Isolation of Microorganism. However, the employment of the streaking methods and pattern of streaking varies from lab to lab.
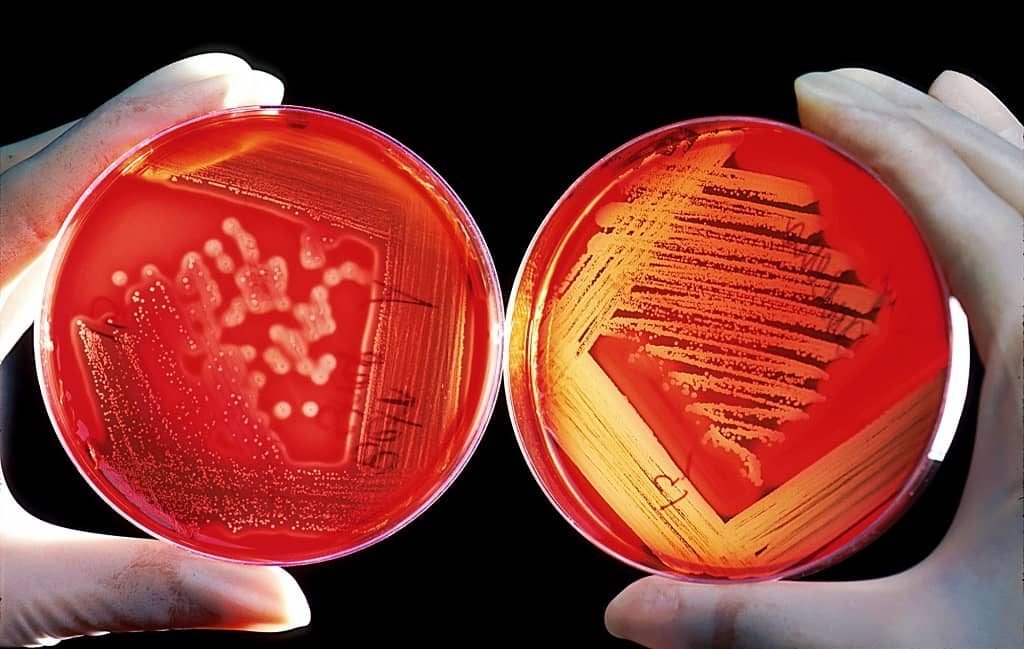
Parallel Streak Quadrant Method
⇒ Hold the Specimen tube or Broth culture tube of mixed culture or the Diluted Specimen tube in the left hand.
⇒ Now, sterilize the inoculating loop in the flame of the Bunsen burner or Spirit lamp, holding in the Right hand. Remove the cotton plug of the tube and immediately flame the mouth of the tube.
⇒ Insert the Sterilized inoculating loop into the broth culture tube and withdraw one loopful of culture.
⇒ Promptly, flame the mouth of the tube, replace the cotton plug and place the tube in the test tube rack.
⇒ Now, hold the solidified sterile media plate in your left hand at an angle of 60° and place the inoculum (the loop containing the droplet of the specimen) on the agar surface in area 1 (at the edge farthest from you).
⇒ Flame the inoculating loop and cool for 5-10 seconds or promptly by touching to the unused area of solidified agar medium in the media plate. Streak the inoculum from side to side in parallel lines across the surface area 1.
⇒ Remove the loop and close the inoculated media plate. Reflame and cool the loop and turn the media plate 90° anti-clockwise and touch the sterilized inoculating loop to a corner of the culture in area 1 and drag it several times across the agar in area 2, hitting the original streak a few times. Remember that the loop should never enter area 1 again.
⇒ Remove the loop and close the inoculated media plate. Reflame and cool the loop and turn the media plate 90° anti-clockwise. Now Streak the area 3 in the same manner as area 2, hitting the last area several times.
⇒ Reflame and Cool the loop and turn the Media plate to 90°. Touch the loop to the corner of the culture streak in Area 3 and streak the inoculum across the agar.
⇒ Finally, the last streak is made in a zigzag manner by touching the corner of the culture streak in area 4 and streaking it in a zigzag manner making a tail in the culture. Remember not to overlap this closing tail with any of the Area of Quadrant.
⇒ Replace the Lid of the Inoculated Media plate and sterilize the inoculating loop in the flame of Bunsen burner or spirit lamp.
⇒ Incubate all the plates at optimum temperature, usually at 37 °C, in an inverted position for 24-48 hours.
Check out the T streak method of Streak Plate Technique for the isolation of Microorganism
Check out the Zigzag Quadrant Method of Streak Plate Technique for the Isolation of Microorganism
Examine the plates for the appearance of individual colonies growing throughout the quadrants in the agar medium. The colonies outside the quadrant are considered as contamination.
RESULTS OF STREAK PLATE CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Generally, a confluent growth will be observed where the initial streak was made, the growth is less dense away from the streak, and discrete colonies will be there in the last area and tail streak.
If the diluted specimen was used to inoculate the media plates, the colonies in the cultures media plates will shows the lesser and lesser no. of the colonies with the increase in dilution factor that means the highest no. of colonies will develop in Plate no. 1 and least no. of colonies in plate no. 6 which will be distributes more or less sparsely along the streak lines.

Select the discrete and well-developed colony and note down the characteristics like Color, Shape, Size, Appearance, Elevation, and Pigmentation etc.
These colonies may be transferred i.e. sub-cultured to the fresh media plates by streaking or other culture techniques to obtain the pure culture of the bacterial cells for further study.
PRECAUTIONS TO BE TAKEN…..
⇒ The protocol should be followed under all aseptic conditions preferably in Laminar Air Flow (Safety cabinet) to avoid any contamination.
⇒ Accurately measure the quantity while preparing the serial dilutions of the specimen.
⇒ Allow the media plates to uniformly solidify. Do not inoculate the specimen on partially solidified media plates.
⇒ Avoid pressing the inoculating loop too firmly against the agar surface.
⇒ The lid of the Petri plate should not be lifted completely to avoid any external contamination.
⇒ Sterilize the inoculating loop properly after streaking in an area of the quadrant to avoid contamination and to get the discrete & well-developed colonies.

Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.
Interesting
Hi Sahil
I like your blogs.