There are so many biochemical reactions for the well known causative agent of Pneumonia and Otitis media infection i.e. the Streptococcus pneumoniae but a few reactions are most commonly used and are medically important for distinguishing pathogenic strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae from other non- pathogenic strains as well as from other species of Streptococcus which are as follows:
⇒ Catalase Negative
⇒ Oxidase Negative
⇒ Alfa- hemolysis on Blood agar
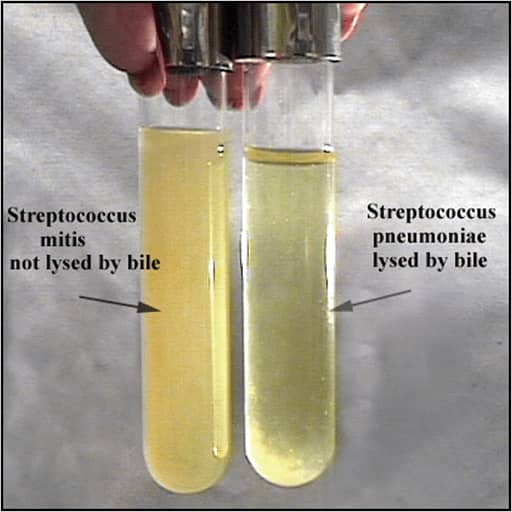
⇒ Soluble in 10% Bile (differentiate S. pneumoniae from S. pyogenes)
⇒ Growth on CVNG (Crystal violet – Nalidixic acid – Gentamycin Agar) medium.
⇒ Fermentation of Inulin (differentiate S. pneumoniae from other Streptococci)
⇒ Sensitive to the Optochin antibiotic (differentiate S. pyogenes from other Hemolytic Streptococci)
Check out the Biochemical tests for Streptococcus pyogenes
Besides that of various biochemical reactions and Sugar fermentation, certain enzymatic reactions are also medically important to distinguish Streptococcus pneumoniae from other Streptococci.
Below is the list of these Enzymatic Reactions and various other biochemical tests for Streptococcus pneumoniae which have great importance in research and for knowledge but are not routinely employed:
| TESTS | RESULTS |
|---|---|
| Bile Solubility | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Hyalurodinase | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Neuraminidase | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Arginine Dehydrolase | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| MR (Methyl Red) | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| VP (Voges Proskauer) | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Coagulase | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Catalase | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Acetoin production | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Indole | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Alkaline Phosphatase | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| PYR | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Urease | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Oxidase | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
Streptococcus pneumoniae and other species of Streptococci ferment various sugars producing acid without gas.
But these sugar fermentation tests are of no diagnostic value in routine laboratory tests except Inulin fermentation test which is of great importance in differentiating Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is Inulin fermentation Positive, from other Pathogenic & non-pathogenic Streptococci especially from Streptococcus pyogenes.

The other sugar fermentation tests which are described below are of great importance in research work.
| SUGARS | RESULTS |
|---|---|
| Arabinose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Erythritol | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Fructose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Galactose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Glucose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Glycogen | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Inulin | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Lactose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Maltose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Raffinose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Sucrose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Xylose | +VE (POSITIVE) |
| Dulcitol | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Hippurate | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Mannitol | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Ribose | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Sorbitol | -VE (NEGATIVE) |
| Trehalose | VARIABLE (depends on strain) |
That’s all about the Biochemical tests for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Further Reading:
Biochemical tests and Identification of S. pneumoniae – Microbiology info
How to identify Streptococcus pneumoniae? – Microbeonline

Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.