MYCOLOGY NOTES – A QUALITY STUDY NOTES OF MYCOLOGY
Mycology is the branch of microbiology that deals with the study of Fungi and Fungal infections are the most abundant and ubiquitous microorganism as that of bacteria that serve as both flora and pathogen to humans. In this section, you will get the study notes of all the topics with detailed and illustrative explanations which are quite easy to understand. Here you will get the study notes on various topics from the basics like the introduction to mycology, characteristics of fungi, its classification, how they are cultured in the laboratory and how the laboratory diagnosis of various fungal infections is accomplished to the study of individual fungi with detailed and illustrative explanation and if you got stuck anywhere or have any queries about any topic contact us here and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Click on the links below to learn more…..

INTRODUCTION TO SUBCUTANEOUS MYCOSES - Subcutaneous mycosis is principally found in tropical and subtropical regions. The fungi causing such subcutaneous mycoses are either normally present in the soil or are pathogens of plants. the various types of subcutaneous mycoses include – Mycotic Mycetoma Sporotrichosis Rhinosporidiosis Chromomycosis Subcutaneous phycomycosis MYCETOMA ⇒ Mycetoma is a chronic, granulomatous, post-traumatic infections of the subcutaneous tissue, usually affects the foot and rarely the other parts ...
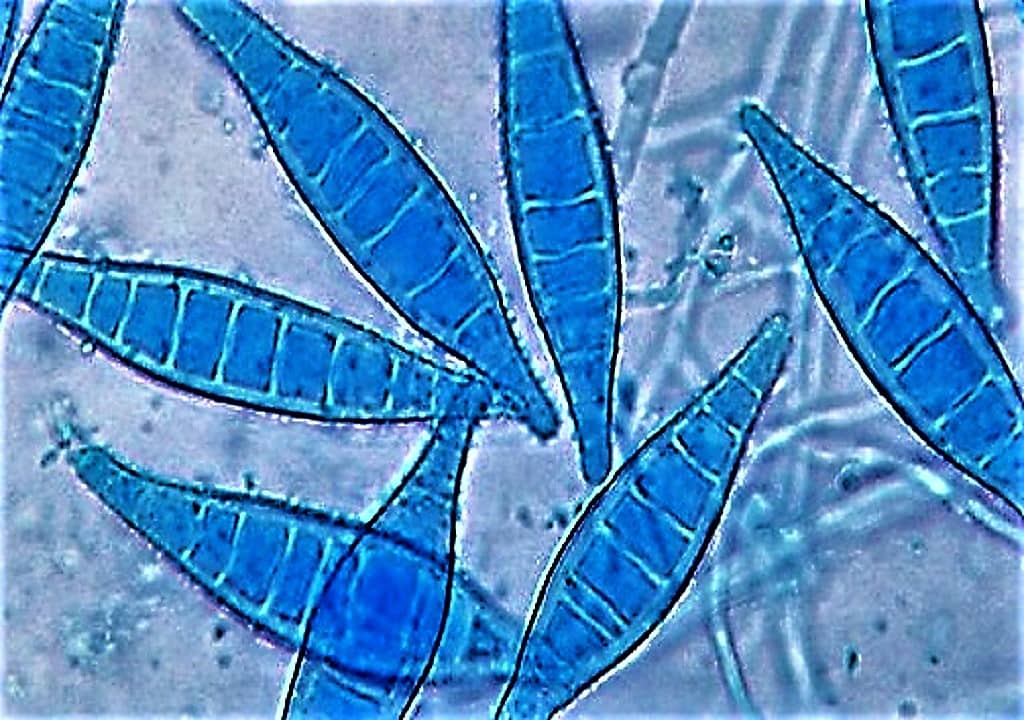
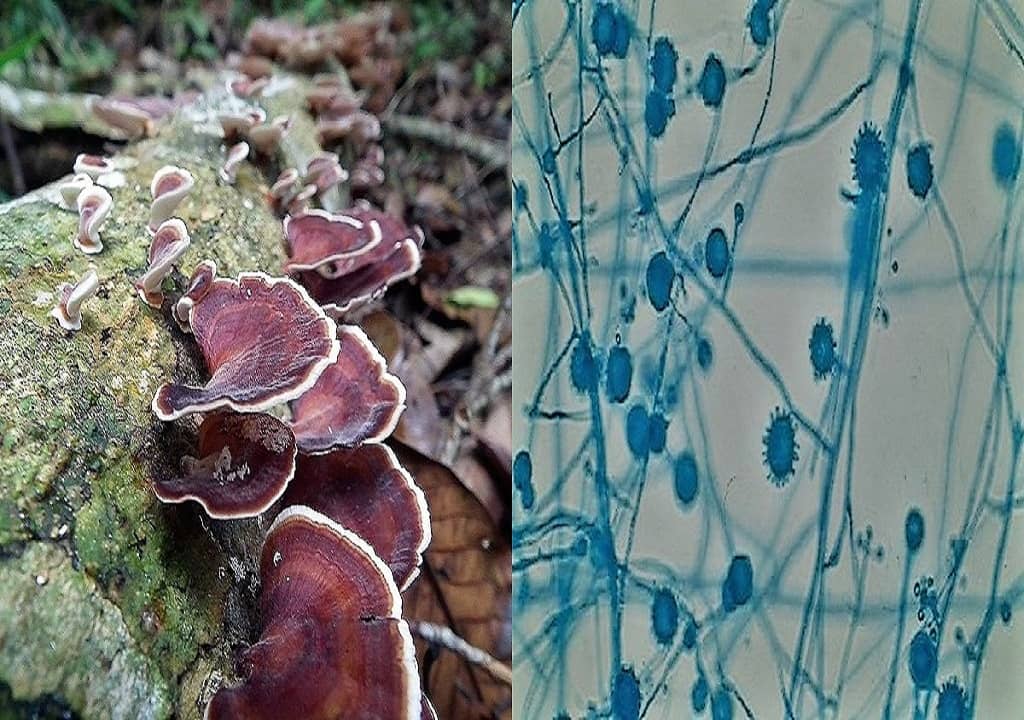
INTRODUCTION TO SUPERFICIAL MYCOSES Superficial mycoses are the infections caused by fungi in the outermost layers of the skin, hair or nails. Superficial mycosis is further classified as:- Surface infections Cutaneous infections A.) SURFACE MYCOSES - ⇒ The fungi live exclusively on the dead layers of the skin, its appendages (Hair & Nail) and mucosa. ⇒ They have no contact with living tissue and elicit no inflammatory response. ⇒ For ...

LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF FUNGI IS CARRIED OUT AS FOLLOWS: ⇒ The laboratory diagnosis of fungi or fungal infections is made by microscopy, culture, serology and skin test (for hypersensitivity). ⇒ Specimens: the specimen is collected from the site of the lesion. In case of disseminated (spreading) infection, blood sample needs to be collected. ⇒ Microscopy: fungal structures can be detected in clinical specimens by direct microscopic examination of material from ...

INTRODUCTION TO MYCOLOGY MYCOLOGY is the branch of microbiology that deals with the study of Fungi and Fungal diseases. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI ⇒ All fungi are Eukaryotic protists. ⇒ They may be Multicellular (Moulds) or Unicellular (Yeasts). ⇒ They are chemotropic organisms i.e. obtaining their nutrients from chemicals in nature. ⇒ Fungi are obligate or facultative aerobes. ⇒ Water, soil, and decaying organic debris are the natural habitat of ...
Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.




