The term “Sputum” often used interchangeably with the “phlegm” but technically if we take a look at these words, they have a little bit of difference as…. the mucus secreted from the Respiratory tract is known as the “Phlegm” whereas When Phlegm is mixed with the Saliva it is termed as “Sputum”.
The Microbiological examination of Sputum is commonly done as sputum is desired in cases of suspected pulmonary tuberculosis (caused by M. tuberculosis), Bronchiectasis, Bacterial pneumonia (caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or Klebsiella pneumoniae), Pulmonary Mycotic infection, and lung abscesses, in case of pneumonia complications and in a variety of systemic diseases that may associated with Respiratory tract.
Let’s start with discussing the principle on which the sputum examination is based and later on we’ll move towards that how it is done in the laboratory which includes the direct microscopic examination of the specimen as well as the Culture of Sputum specimen followed by the observations and results of the test…..
PRINCIPLE OF SPUTUM EXAMINATION
The sputum specimen can be examined by Gram stain method, Acid fast staining method and also the Sputum culture is often done on blood agar plate and Tubes of Thioglycollate medium to isolate the microbe that might be associated with the ailment. After inoculating the specimen on media plates & tubes, they are incubated in Anaerobic and aerobic conditions at 37 °C at least for 24-48 hours.
The growth on the culture media plates can be identified based on the colony morphology, biochemical reactions and appropriate staining procedures which reveals everything about the microbe so that the doctor can easily prescribe an effective treatment.
MATERIAL REQUIRED FOR THE EXAMINATION OF SPUTUM SPECIMEN IN MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY
- Tube of Thioglycollate medium
- Blood Agar Plate
- LJ medium (if the Sputum culture for Mycobacterium is advised by the Dr.)
- Gram stain reagents
- Acid – Fast reagents
- Candle Jar
- Inoculating loop
- Glass Slide
- Spirit lamp
DIRECT MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION OF SPUTUM SPECIMEN
⇒ Transfer a loopful of the sputum specimen on clean, grease-free and sterilized microscopic glass slide.
⇒ Carefully, Press another clean and sterilized glass slide on top of the above slide.
⇒ Gently Squeeze the two glass slides together and pull them apart.
⇒ Immediately Air dry the Slides and after air drying, flame both the slides promptly 2-3 times.
⇒ Stain one slide by the gram staining technique.
Check out the Gram Staining Technique
⇒ Stain the second slide by the Acid Fast staining technique.
Check out the Acid Fast Staining Technique
Observations & Results
Observe both the slides under the oil-immersion objective of the microscope. The Gram stain preparations will show the gram-positive and gram negative bacteria while Acid fast preparations show the Acid-fast and Non-acid fast bacteria which appears as follows:
⇒ Gram-positive – Purple Color
⇒ Gram-Negative – Pink Color
⇒ Acid-fast bacteria – Red color
⇒ Non-Acid fast bacteria – Blue color

CULTURE OF THE SPUTUM SPECIMEN
⇒ Streak the Sputum specimen on the Blood agar plate using a well sterilized inoculating loop.
⇒ Inoculate Thioglycollate tube with small loopful of a selected portion of the sputum.
⇒ Place the inoculated blood agar plate in a candle jar (Anaerobic condition).
⇒ Incubate the jar (with inoculated plate) and the Thioglycollate tube at 37 °C for 24-48 hours.
⇒ After incubation mix the contents of Thioglycollate tubes.
⇒ Transfer a loopful of the inoculum to another blood agar plate.
⇒ Incubate the inoculated blood agar plate (Kept in candle jar) at 37 °C for 24-48 hours.
Observations & Results
Observe the plate and tube daily for the growth of the microorganisms. If Small, Shiny, Greenish, Transparent flat colonies with depressed centers and raised margins observed on blood agar plate will most likely belong to Pneumococci (Most commonly observed). Alpha hemolytic and Non-hemolytic streptococci may also be seen.
CULTURE OF THE SPUTUM SPECIMEN FOR THE ISOLATION OF MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS
⇒ The Sputum culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a time taking process because M. tuberculosis takes at least 2 – 4 weeks to form colonies as the generation time of this bacterium is 14 – 15 hours.
⇒ For this purpose, the selective medium for the M. tuberculosis is used which is Lowenstein Jensen (LJ) Medium.
⇒ The Sputum specimen is inoculated on the LJ medium and incubated in an aerobic environment at 37 °C at least for 2 weeks.
Results of Sputum Culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Observe for the growth appears on the surface of the LJ medium. Mycobacterium tuberculosis forms a Dry, rough, Buff colored, Raised colonies with a wrinkled surface.
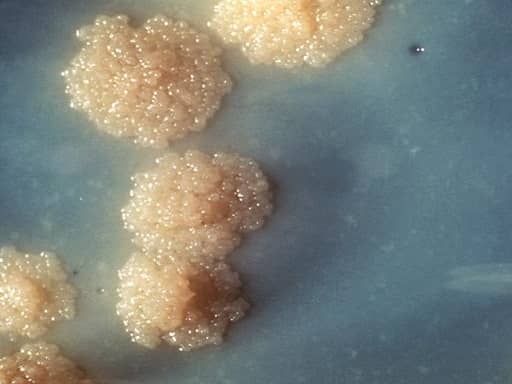 COLONIES OF MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS ON LJ MEDIUM
COLONIES OF MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS ON LJ MEDIUM
That’s all about the Examination of Sputum specimen in Microbiology laboratory
Check out the Interpretation of result and Reporting of AFB in sputum Specimen

Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.
What if Blood is present in the sputum Phlegm.? Does the Blood have to be separated and tested?