INTRODUCTION TO MUMPS VIRUS
⇒ MUMPS VIRUS is the causative agent of disease MUMPS, an acute infectious disease commonly affecting children and characterized by Parotitis (inflammation of parotid glands).
⇒ It had been described by Hippocrates in the fifth century BC as ‘Epidemic Parotitis’.
⇒ This virus belongs to the Rubulavirus genus of Paramyxoviridae
MORPHOLOGY OF MUMPS VIRUS
⇒ It Resembles orthomyxovirus in morphology – Spherical, Enveloped virus with helical Nucleocapsid (13-18 nm).
⇒ Size: 100-250 nm in diameter.
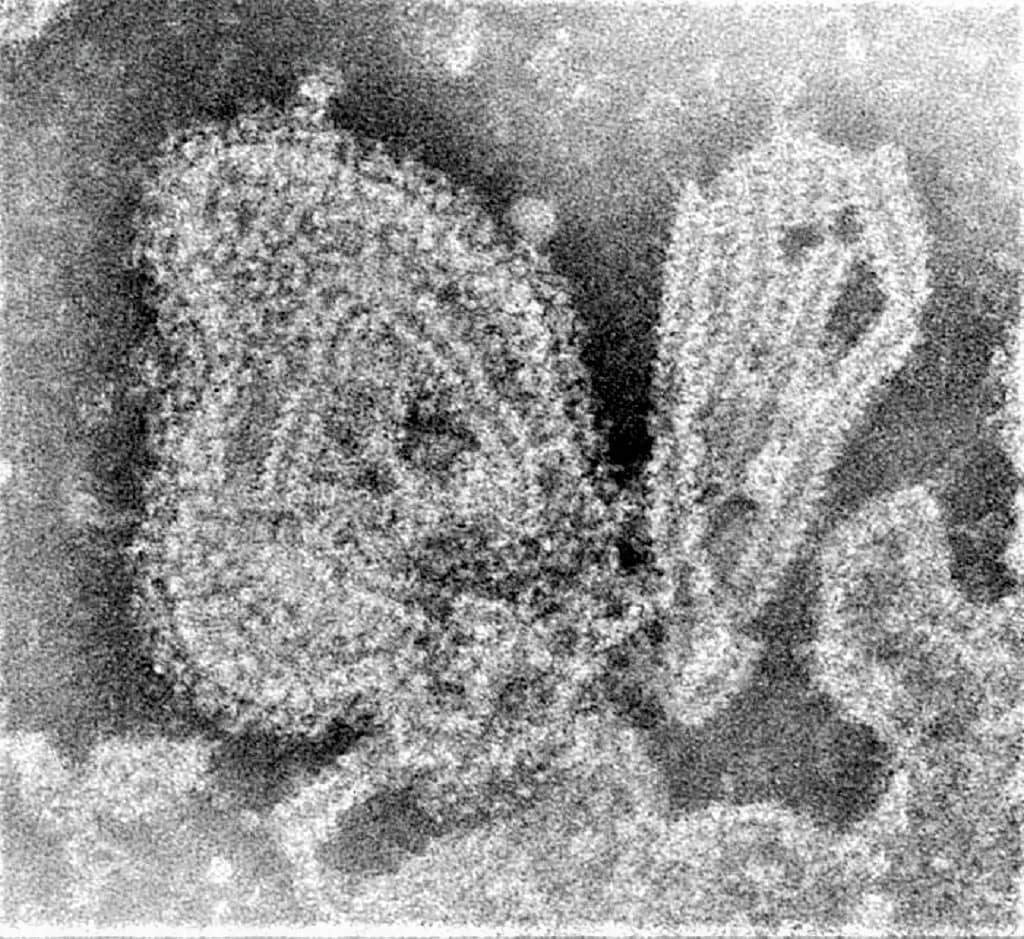
⇒ The envelope is covered by projections of HN (Hemagglutinin, Neuraminidase) and F (Fusion protein) peplomers.
⇒ Genetic Material:- Linear ssRNA
⇒ There is only one serotype of Mumps virus.
RESISTANCE SHOWN BY MUMPS VIRUS
⇒ The mumps virus is labile, rapidly inactivates at room temperature.
⇒ Exposure to formaldehyde, ether or ultraviolet light inactivates the virus particle.
⇒ It can be preserved at –70oC or by lyophilization.
PATHOGENESIS OF MUMPS VIRUS
⇒ This virus causes the disease mumps, an acute infectious disease characterized by non-suppurative enlargement of the parotid gland and Parotitis.
The virus is Acquired by Inhalation and
through the conjunctiva.
⇓
The virus replicates in upper respiratory tract &
Cervical lymph nodes.
⇓
Disseminated through the bloodstream to
Various organs cause swelling & Inflammation.
CLINICAL FEATURES OF MUMPS VIRUS INFECTION
⇒ The incubation period of this virus is 12-25 days.
⇒ Parotid swelling is usually the first sign of illness preceded by Malaise
⇒ It is accompanied by Fever, Local pain, and tenderness of parotid gland and Parotitis.
⇒ Epididymo-orchitis and Meningoencephalitis are important complications of Mumps.
⇒ Other less common complications are Arthritis, Oophoritis, Nephritis, Pancreatitis, Thyroiditis, and Myocarditis.
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF MUMPS VIRUS
⇒ Specimen: Saliva, Throat secretions, CSF and Urine.
⇒ Direct Demonstration: Immunofluorescence on secretions of throat and saliva.
⇒ Isolation of the virus: Virus can be isolated from saliva, Throat swab, CSF or urine by inoculating into Primary monkey Kidney, HEp-2 or in Human Amnion.
⇒ Serology: Mumps specific IgM antibodies can be detected in serum by ELISA. Hemagglutination Inhibition Test and Neutralization Test can also be done.
PROPHYLAXIS OF MUMPS VIRUS
⇒ MMR, a live attenuated, vaccine is available. It can be administered subcutaneously and is a combination of attenuated Mumps, Measles and Rubella vaccine.
⇒ This vaccine is given to children aged 12-15 months.
⇒ It provides effective protection for at least 10 years.

Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.
the website is wonderful. it has all the topics of our needs