Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram +ve, round shape bacteria that are arranged in grape-like clusters. The organisms of this genus are the commonest cause of suppurative lesions.
It was first isolated by Sir Alexander Ogston and he gave the name Staphylococcus for the typical arrangement of the cocci in grape-like clusters.
There are about 40 species of Staphylococcus exists in nature but the medically important species for humans includes –
- Staphylococcus aureus – pathogenic, causes pyogenic infections
- Staphylococcus epidermidis – Skin commensal
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus – opportunistic pathogen
The pathogenic species of Staphylococcus i.e. S. aureus have certain characteristics like the production of enzymes Coagulase, Phosphatase, Deoxyribonuclease and ability to ferment mannitol sugar. These tests are really helpful in differentiating S. aureus from other species.
Also, Staphylococci are classified on the basis of Coagulase enzyme production as Coagulase +ve and Coagulase –ve.
There are various strains of Coagulase +ve Staphylococcus which produce Golden yellow colonies on the Nutrient agar media (NAM) and are called as Staphylococcus aureus or simply Staph aureus. These strains are toxigenic and cause various pathologies in humans.
The Coagulase –ve strain strains that are non-pathogenic and non-toxigenic to humans, produce white color colonies on Nutrient agar medium (NAM) and are called Staphylococcus epidermidis. This species of Staphylococcus was earlier termed as Staphalbus by Rosenbach.
The third medically important species of Staphylococcus i.e. S. saprophyticus which is an opportunistic pathogen is a Coagulase –ve species and produces Lemon yellow color colonies on the Nutrient agar medium (NAM) and earlier termed as staphcitreus by Passet.
Click on the links below to learn more…..

MORPHOLOGY AND CULTURE CHARACTERISTICS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS

BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (S. aureus)
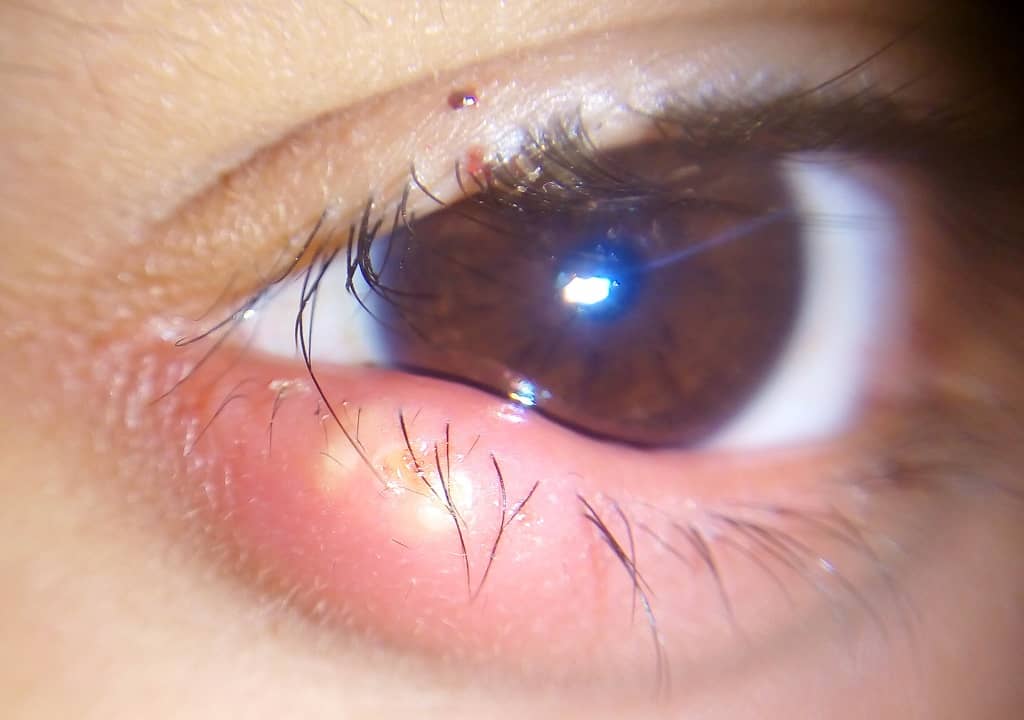
TOXINS AND PATHOGENESIS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS

LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS

Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.
You are a blessing in disguise, thanks a million.
Love the pictures. I learn so much from visual…With text..