INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS VIRUS
⇒ Viral hepatitis is a systemic disease with primary inflammation in the liver by any one of a heterogeneous group of hepatitis viruses.
⇒ There are six hepatitis viruses i.e., hepatitis A, B, C, D, E & G.
⇒ The designation ‘type F’ had been proposed for a putative virus believed to cause transfusion-associated hepatitis, later proved to be the mutant (HBx) of the type B virus & not a separate entity. Due to this reason type F was deleted from the list of hepatitis viruses.

HEPATITIS A VIRUS (HAV) – MORPHOLOGY, TRANSMISSION, CLINICAL FEATURES & LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS A VIRUS (HAV) ⇒ Hepatitis A virus (HAV) was first demonstrated by the Feinstone & co-workers in 1973 by using immunoelectron microscopy (IEM). ⇒ HAV causes Type A hepatitis or Infectious Hepatitis, a subacute disease occurring mainly in children & young adults. MORPHOLOGY OF HEPATITIS A VIRUS ⇒ HAV is a 27 nm, non-enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus with an icosahedral symmetry. ⇒ HAV belongs to the Picornavirus ...
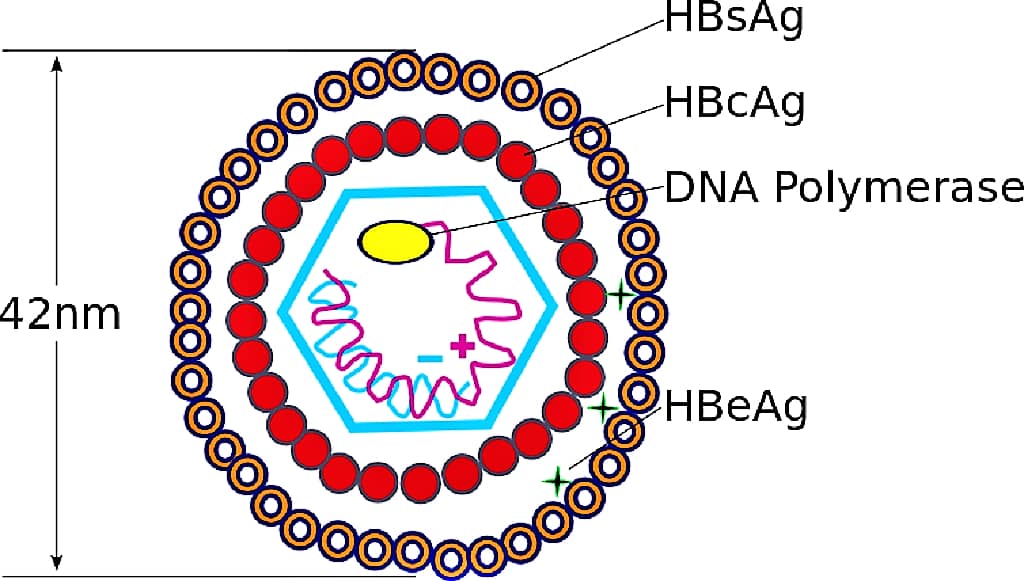
HEPATITIS B VIRUS (HBV) – MORPHOLOGY, TRANSMISSION, CLINICAL FEATURES & LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS B VIRUS (HBV) ⇒ HBV was first observed in 1965 & named as Australia antigen. Later, in 1968, it was found to be associated with serum hepatitis & the name has been changed to Hepatitis B Virus (HBV). ⇒ HBV causes Type B hepatitis, the most widespread and the most important type of viral hepatitis. ⇒ HBV is the only hepatitis virus that contains DNA as genetic ...

HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) – MORPHOLOGY, TRANSMISSION, CLINICAL FEATURES & LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) ⇒ HCV was identified during the research for ‘non-A non-B’ viruses by experimental infection in the chimpanzees. ⇒ HCV is the most common cause of post-transfusion hepatitis in the developed countries. ⇒ Infection due to Hepatitis C virus is seen only in humans. MORPHOLOGY OF HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) ⇒ HCV belongs to Hepacivirus genus of Flaviviridae ⇒ Size – 50-60 nm in diameter ⇒ ...

HEPATITIS D VIRUS (HDV) – MORPHOLOGY, TRANSMISSION, CLINICAL FEATURES & LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS D VIRUS (HDV) ⇒ HDV was identified in 1977 by Rizzetto & colleagues in the liver cell nucleus, as a new viral particle, of the patient infected by HBV and named as Hepatotropic virus Delta or Hepatitis D virus (HDV). ⇒ HDV is a defective virus as it depends on the helper function of HBV for its replication and expression. ⇒ HDV causes Type D Hepatitis & ...

HEPATITIS E VIRUS (HEV) – MORPHOLOGY, TRANSMISSION, CLINICAL FEATURES & LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS E VIRUS (HEV) ⇒ Type E hepatitis is caused by the Hepatitis E Virus, responsible for the majority of the epidemic and sporadic hepatitis in adults. ⇒ It is also known as the NANB – ‘Nor A Nor B’ virus or E-NANB – the enterically transmitted NANB virus. ⇒ HEV infection often appears as epidemics, also known as Epidemic NANB. MORPHOLOGY OF HEPATITIS E VIRUS (HEV) ⇒ HEV ...
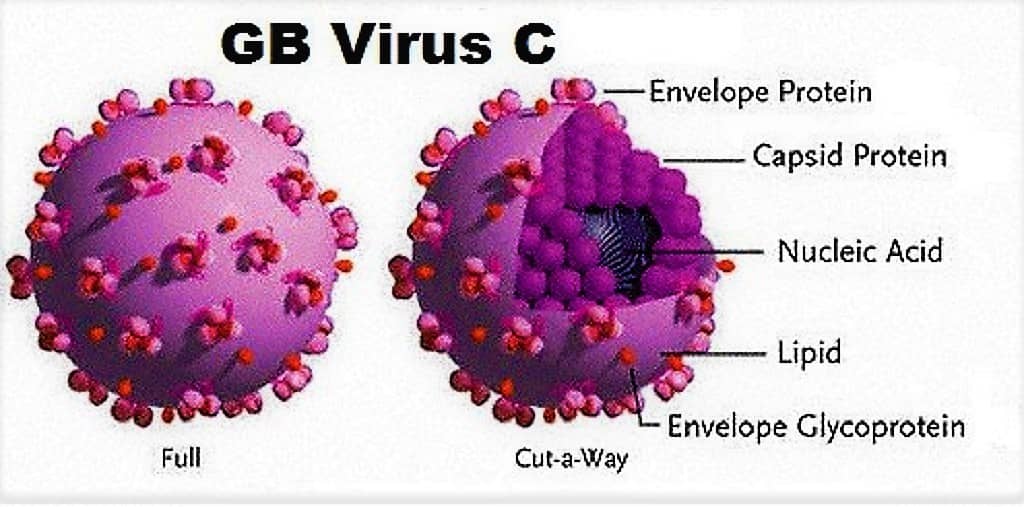
HEPATITIS G VIRUS (HGV) – MORPHOLOGY, CLINICAL FEATURES & LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO HEPATITIS G VIRUS (HGV) Hepatitis G Virus causes the Type G Hepatitis, HGV was first observed in 1995 and described as GBV type C, later in 1996 has been found to be associated with chronic hepatitis and named as HGV. MORPHOLOGY OF HEPATITIS G VIRUS (HGV) ⇒ HGV belongs to Flaviviridae ⇒ HGV is a Spherical, non-Enveloped virus. ⇒ Genetic material – ssRNA. CLINICAL FEATURES OF TYPE G HEPATITIS ...

Hi, I’m the Founder and Developer of Paramedics World, a blog truly devoted to Paramedics. I am a Medical Lab Tech, a Web Developer and Bibliophiliac. My greatest hobby is to teach and motivate other peoples to do whatever they wanna do in life.
Well outline pic and easy to identify each virus
I have gained a lot from your e mails thank you.
Thanks for the in depth knowledge on this topic. It was fun to read.